ACTFL-Scale Levels of Language Proficiency
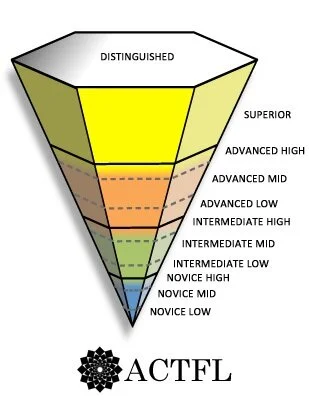
The ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines were updated in 2012 by ACTFL to break down language skills in multiple domains into levels of language proficiency. There are a total of eleven ACTFL levels of language proficiency levels that fit into five primary proficiency levels, Novice, Intermediate, Advanced, Superior, and Distinguished. Within the Novice, Intermediate, and Advanced levels there are three subdomains (Low, Mid and High). You can see the breakdown of the ACTFL levels of language proficiency in the image below.
ACTFL Levels from lowest to highest:
Novice Low
Novice Mid
Novice High
Intermediate Low
Intermediate Mid
Intermediate High
Advanced Low
Advanced Mid
Advanced High
Superior
Distinguished
Read below to learn more about each level.
ACTFL-Scale Levels of Language Proficiency Explained
Novice Low: This level is characterized by an ability to understand and produce isolated words or high-frequency phrases, often with significant errors. It's the beginning level of language acquisition.
Novice Mid: At this level, individuals can express basic personal information and needs, primarily through memorized phrases and a limited amount of learned words and structures.
Novice High: At this level, an individual can communicate short messages on highly predictable, familiar every day topics that affect them directly. They can piece together vocabulary to create strings of sentences but rely heavily on memorized and learned phrases.
Intermediate Low: Individuals at this level can manage simple, predictable communication necessary for survival in the target language, such as personal information, basic needs, and common everyday contexts. They can ask and answer questions but may struggle to understand or be understood by native-speakers unaccustomed to non-native speakers.
Intermediate Mid: This is a level where individuals can handle basic communicative tasks in straightforward social situations. They can ask and answer questions with some detail about themselves and their immediate environment (travel, lodging, food, shopping). Their language is characterized by strings of sentences that use high-frequency and simpler grammatical structures.
Intermediate High: Individuals at this level can handle uncomplicated tasks and social situations requiring an exchange of information related to their work, school, recreation, etc. They can be understood by native speakers despite errors and interference from their native language. They can provide paragraph-length narratives in past, present, and future but with inconsistency.
Advanced Low: Individuals can handle basic communicative tasks for work, academic, or social situations. They can communicate clearly in multiple time frames, but their native language still interferes with the use of false cognates, literal translations, and paragraph structure, and their speech may include a large amount of self-correction.
Advanced Mid: At the Advanced-Mid level, an individual has the capability to handle a variety of communicative tasks, albeit with some errors. Individuals can handle concrete exchanges and discussions on a range of concrete topics, and be fully understood by a native speaker. They can competently narrate and describe in past, present, and future with organized, extensive detail and supporting examples.
Advanced High: At the Advanced-High level, an individual can communicate with accuracy and fluency in the language, expressing themselves in most informal and formal settings. They may occasionally make mistakes in low-frequency or highly complex grammatical structures but possess multiple strategies that compensate for vocabulary gaps.
Superior: At the Superior level, an individual can speak the language with near-native fluency and accuracy sufficient for use in formal and professional conversations, including technical discussions in their field of expertise. They can handle both concrete and abstract concepts and are able to fully participate in extended argumentation on a variety of topics.
Distinguished: At the Distinguished level, an individual demonstrates exceptional native-speaker fluency and accuracy in the language, capable of using it effectively in a broad range of highly demanding, professional situations. Their language includes cultural and historical references, is extended, and is highly organized.
Curious About Your Proficiency Level?
The Global Seal of Biliteracy has developed a free adaptive self-assessment based on the commonly used NCSSFL-ACTFL Can-Do Statements. These can-do statements are reflective of an individual’s language ability based on the ACTFL-Scale Levels of Language Proficiency.
Credential Your Language Skills
The Global Seal of Biliteracy language credential creates a three level award pathway at the Functional (Intermediate-Mid), Working (Advanced-Low) or Professional Fluency (Advanced-High) level that correlates with the ACTFL levels of language proficiency. To learn more about the Global Seal of Biliteracy click the learn more button below.